Wetin be layer 2 blockchain?

Layer-two blockchain na technology (new things) wey dey build on top of layer-one blockchain to make mata dey go fast fast and cheaper. Dem no dey write down every money mata for the main blockchain; instead, dem dey do some transactions off-chain (outside the main blockchain) to reduce the time and cost. If wahala happen, dem go use the main blockchain as backup. Dis way, money mata fit go through fast fast, the fees go reduce, and the blockchain go fit handle more money mata. Na like extra layers wey dey help the main blockchain work better.
Dis method make di transaction load for di main blockchain reduce and e still work well with di old system. Di speed of transactions depend on di communication speed and delay of di people wey dey involved. Di security of di off-chain transactions fit dey guaranteed by using some money as collateral, like for payment channels, or by delaying di final approval of transactions for commit chain designs.
Layer-two protocols (rules) dey build on top of layer-one blockchains. Dem no dey send every money mata to di whole network; instead, dem dey exchange money mata wey dem don check well, well off-chain (something wey no dey main chain). Dem go use the blockchain only if wahala (dispute) happen. The main idea be sey layer-two rules fit complete money mata off-chain in fast fast, like for seconds, instead of minutes or hours. Dem go still keep your money safe, reduce fees, and help blockchains grow.
Different types of layer-2 blockchain dey wey fit help make transactions faster and cheaper. Here be some of dem:

- State Channels: Na two-way communication channels wey fit do transactions off-chain (outside di main blockchain). Dem good for frequent transactions like gaming or streaming services. Transactions dey happen instantly and privately, but dem need make funds dey locked up and trust between di people involved.
- Sidechains: Na independent blockchains wey dey run side by side with di main chain, wey dey connected through wetin dem dey call two-way peg. Dem dey allow specific applications wey need different parameters from di main chain. Sidechains get customizable features and independent governance, but di security dey depend on di sidechain’s own consensus mechanism.
- Rollups (Optimistic and zk-Rollups): Dem dey combine many off-chain transactions into one main chain transaction. Optimistic Rollups assume say transactions dey valid by default and only check for fraud under some conditions, while zk-Rollups use cryptographic proofs to validate transactions. Both types dey improve efficiency and privacy, but zk-Rollups dey more complex to develop, and Optimistic Rollups get withdrawal delay.
- Plasma: Dis framework dey create child chains off di main Ethereum chain. E dey allow make smaller, more manageable blockchains dey handle transactions and den dey report back to di main chain periodically.
Dese layer-2 solutions dey help reduce di load on di main blockchain, making transactions faster and cheaper while still benefiting from di security of di main chain.
Di four different layers we make up blockchain:
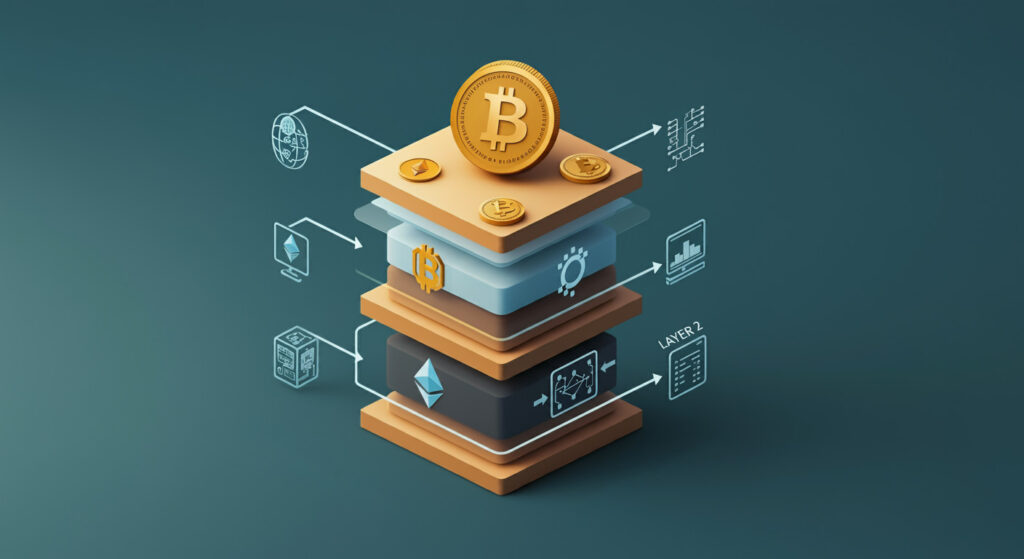

- Layer 0: Dis na di foundation wey dey for under di blockchain. E be like di internet or di hardware wey dey support di whole blockchain network. Without layer 0, blockchain no go fit work.
- Layer 1: Dis na di main blockchain wey everybody dey see and use. E dey handle di transactions, security, and decentralization. Popular examples be Bitcoin and Ethereum. Na here we dey do di main recording of all money mata.
- Layer 2: Dis one dey on top of layer 1 to make money mata faster and cheaper. E dey offload some transactions from di main blockchain to reduce load and increase speed. Example na Lightning Network for Bitcoin and Plasma for Ethereum. E dey help make di whole system scale better.
- Layer 3: Dis na di application layer wey dey on top of layer 2 and 1. E dey include di apps and smart contracts wey people dey use. Na here you go see things like decentralized finance (DeFi) apps, games, and other blockchain-based applications.
For DeFi apps, some examples be:
- Aave: Dis na decentralized lending and borrowing platform wey allow users to earn interest for deir cryptocurrency investment portfolio.
- Uniswap: Dis na popular decentralized exchange (DEX) wey make am easy for people wey dey use am to exchange different cryptocurrencies without (middleman) oga wey dey collect commission.
- MakerDAO: Dis one dey provide stablecoin (like DAI) and also allow users to take out loans wen dem use deir crypto as collateral.
- Compound: Another lending platform wey offer automatic interest wey go make your money dey grow well well.
For blockchain games, some examples be:
- Axie Infinity: Dis na game wey dey allow players to collect, breed, and battle cute monsters called we dem dey Axies.
- CryptoKitties: Dis na popular game wey dey allow players to collect and breed special virtual cats.
- The Sandbox: Dis na virtual world game wey dey allow players to create, own, and make money deir gaming skills we dem get.
- Decentraland: Na virtual reality platform wey dey allow users to buy land, build on am, and do online tin with oder users.
Security Threats wey dey Layer 2 Blockchain
For layer-two blockchains, some security threats wey we dey face:
- Channel Attacks: For solutions like Lightning Network, bad people fit try to steal money from payment channels.
- Smart Contract Weaknesses: If dem no write di smart contracts well, hackers fit take advantage of am.
- Double Spending Attacks: Dis one dey happen wen person try spend same money two times, once off-chain and once on-chain.
- Centralization Risks: Dis na wen too few people dey control di layer-two network, e fit reduce decentralization and make di system less safe.
Dese threats show say we need to dey careful and make we dey always dey make beta security arrangements for layer-two blockchains.
Blockchain Three-way wahala (Trilemma)
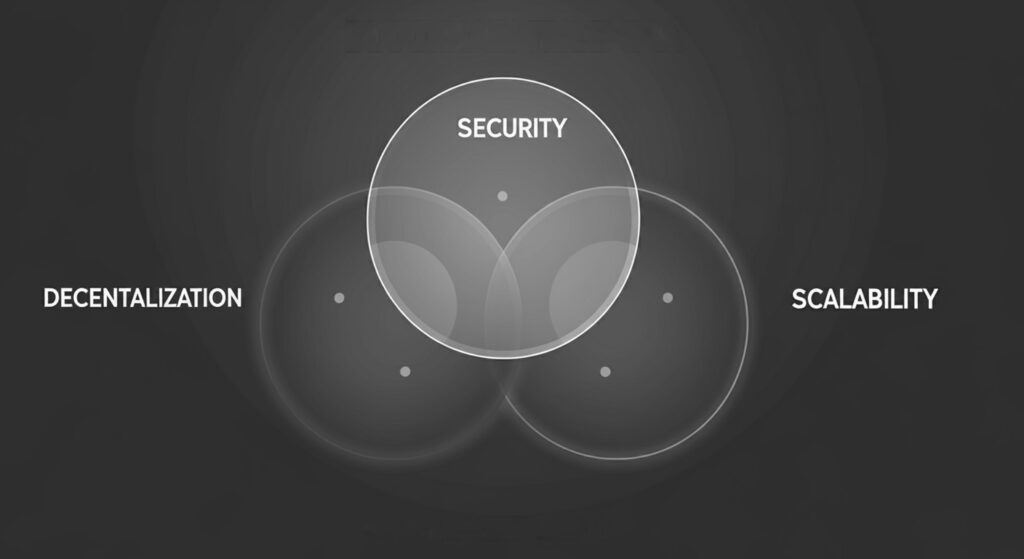
Blockchain trilemma na di wahala wey dey between three important things for blockchain: decentralization, security, and scalability. Di problem be sey e hard to get all three together at di same time for one blockchain system. Here be how e be:
- Decentralization: Dis one mean sey no one person or group dey control di network. Everybody wey dey part of di blockchain get equal power. E make di system fair and transparent.
- Security: Dis one mean say di blockchain dey safe from hackers and bad people. E dey protect di transactions and di data wey dey on top di blockchain.
- Scalability: Dis one mean say di blockchain fit handle plenty money mata quick quick and e no go slow down.
Di trilemma be sey if you focus on two out of these three, di third one go suffer. For example:
- If you make di blockchain decentralized and secure, e go slow down and no fit handle plenty money mata (no scalable).
- If you make am scalable and decentralized, e fit no too secure.
- If you make am secure and scalable, e go fit dey under the control of few people (no decentralized).
So, di challenge na how to balance all three things: decentralization, security, and scalability so dat one of no go dey left behind. Na wetin dem dey try solve for di blockchain world.
Conclusion

To make di long story short, layer-2 blockchain na powerful solution wey fit help make transactions faster, cheaper, and more scalable. Dem dey build on top of di main blockchain (layer 1) to reduce di load and improve performance. Different types dey, like state channels, sidechains, rollups, and Plasma, and each one get their own way wey dem take dey handle money mata off-chain. With layer-2 solutions, we fit enjoy di benefits of blockchain without di wahala of high fees and slow transactions. E dey help make blockchain technology better for everybody.


